之前一致没看严奶奶《数据结构》这本书上的排序这一部分,今天看了一下这一章的内容,里面的快速排序一上来的我看蒙了,怎么和我之前学的快速排序不一样???
为了弄清楚到底哪个是快排的标准写法,我“考古”了一下C. A. R. Hoare大佬1960年快排的论文,发现和我学会的快排又不一样(我是看《算法》这本书学的快排),三个版本的快排 。
。
这一下子兴趣就起来了,这三个到底有啥区别。(突然想到《孔乙己》,“茴字有四样写法,你知道么?”,快排有三种写法(好像不止三种),你知道么? )
)
下面我先写一下三个快排的大体思想。
论文原版快排
论文原文下载地址:点击下载
找一个“标兵”$bound$(如第一个元素),两个指针,一个$i$,指向数组开始,一个$j$,指向数组最后一个元素,$i$先动,从左边找一个小于$bound$的值,然后$j$再动,找一个大于$bound$的值,然后交换两个指针指向的元素,如此反复,直到$i$和$j$两个指针“擦肩而过”,“标兵归位”(标兵与当前$j$指向的元素交换),至此,结束一轮,再递归对两边执行该操作。
严奶奶版快排(建议考研参考此方法)
找一个“标兵”$p$(第一个元素),两个指针,一个$i$,指向数组开始,一个$j$,指向数组最后一个元素,$j$先动,从右边开始找一个大于$p$的值,直接赋值给当前$i$指向的元素(因为$i$指向的元素已经复制给$p$临时保存,所以不会丢失),然后$i$再动,从左边找一个小于$p$的值,直接赋值给当前$j$指向的元素(刚刚这个值已经赋给了,之前$i$指向的位置,所以当前$j$指向的值也不会丢失),如此反复,直到$i >= j$时,将$p$赋值给当前$i$指针指向的位置,至此,结束一轮,再递归对两边执行该操作。
算法(第四版)中的快排(网络上广为流传的版本)
找一个“标兵”$v$(第一个元素),两个指针,一个$i$,指向数组开始,一个$j$,指向数组最后一个元素,$j$先动,从右边开始找一个大于$v$的值,然后$i$再动,从左边开始找一个小于$v$的值,然后交换两个指针指向的元素,如此反复,直到$i >= j$时,将$v$和当前$j$指针指向的元素交换,至此,结束一轮,再递归对两边执行该操作。
三种对比
论文原版是左指针先动,右指针再动,严奶奶和《算法》这本书中的是右指针先动,左指针再动。手动模拟一趟排序过程可以发现,论文原版和《算法》中的中间结果一样,严奶奶的与这两个不同。一般在考试中,排序考的就是中间结果,国内大学又多以严奶奶的书为教材或参考书,所以在期末或者考研中建议还是按严奶奶的方法来(或者其他指定的参考书)。想想之前我数据结构这门课的实际分数和我预期分数的差异,好像知到是因为哪里写错了。
此处应该有模拟一趟排序的图,但博主太懒还没画,先占个空,可以自己随便写个数组画画哈,不想画还急着看文末评论踢我一下。
性能对比
从理论分析上来看,最好情况都是$O(NlogN)$,最坏情况都是$O(N^2)$,但时从算法思路和手动模拟过程,就能看出来,原版会发生两个指针“擦肩而过”,会进行不必要的遍历,所以性能应该会低一些。下面直接从实际对比三种快排算法。
使用随机数函数生成$10^6$个数据,然后排序测试,结果如下: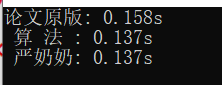
意料之中,论文原版性能最差,严奶奶的和《算法》中的五五开。
当数据量达到$10^7$时候,结果如下: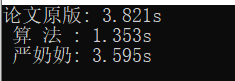
《算法》中的快排比另外两个快了一半!
测试代码(一开始只是打算测试看看,解答自己的疑惑,所以命名比较随意,勿喷):
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
// 内联函数,要多次交换元素,调用次数多,防止函数调用开销影响最后结果
inline void swap(int* x, int* y) {
int temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
//////////// 严奶奶版本开始 ///////////
int partitionYan(int* arr, int low, int high) {
int p = arr[low];
while(low < high) {
while(low < high && arr[high] >= p)
high--;
arr[low] = arr[high];
while(low < high && arr[low] <= p)
low++;
arr[high] = arr[low];
}
arr[low] = p;
return low;
}
void QuickSortYan(int* A, int low, int high) {
int q;
if(low < high)
{
q = partitionYan(A, low, high);
QuickSortYan(A, low, q-1);
QuickSortYan(A, q+1, high);
}
}
//////////// 严奶奶版本结束 ///////////
//////////// 论文原版开始 ///////////
int Partition(int* A, int low, int high) {
int i = low, j = high;
// choos a bound
int bound = A[low];
while(1) {
// lower pointer start first, when the item equal to or less than bound, move upper
while(A[i] <= bound && i<=j) i++;
// then upper pointer start, when the ietm equal to or greater than bound, move lower
while(A[j] >= bound && i<=j) j--;
// The process continues until the pointers cross each other
if(i >= j)
break;
// exchange
swap(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
// The aim is now to produce a situation in
// which the keys of all items below a certain dividing line are equal to or less than the bound,
// while the keys of all items above the dividing line are equal to or greater than the bound.
// 所有元素交换完成后,要将 bound 放到两个 子数组的中间,以满足上述要求
A[low] = A[j];
A[j] = bound;
return j;
}
void QuickSort(int* A, int low, int high) {
int q;
if(low < high)
{
q = Partition(A, low, high);
QuickSort(A, low, q-1);
QuickSort(A, q+1, high);
}
}
//////////// 论文原版结束 ///////////
//////////// 《算法》版本开始 ///////////
int partition(int* a, int lo, int hi) {
int i = lo, j = hi + 1;
int v = a[lo];
while(true) {
while(a[++i] < v)
if(i == hi)
break;
while(a[--j] > v)
if( j == lo)
break;
if(i >= j) break;
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
swap(a[lo], a[j]);
return j;
}
void QuickSortA(int* A, int low, int high) {
int q;
if(low < high)
{
q = partition(A, low, high);
QuickSortA(A, low, q-1);
QuickSortA(A, q+1, high);
}
}
//////////// 《算法》版本结束 ///////////
int main() {
clock_t start, end;
unsigned seed;
seed = time(0);
srand(seed);
int size = 1e7;
int* data1 = new int[size];
int* data2 = new int[size];
int* data3 = new int[size];
// 制造数据
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
data1[i] = rand();
data2[i] = data1[i];
data3[i] = data1[i];
}
// QuickSort:论文原版
// QuickSortA: 算法第四版
// QuickSortYan: 严奶奶版
start = clock();
QuickSort(data1, 0, size-1);
end = clock();
cout<< "论文原版: " << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
start = clock();
QuickSortA(data3, 0, size-1);
end = clock();
cout<< " 算 法 : " << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC<< "s" << endl;
start = clock();
QuickSortYan(data2, 0, size-1);
end = clock();
cout<< " 严奶奶: " << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC<< "s" << endl;
return 0;
}
十年之约-虫洞穿梭与此,期待回访!
@Teacher Du :
学习到了,每天看看博主文章,学习颇多。
@布衣者 : 一起加油变强
感谢博主的分享,支持了。
@马内 : 感谢支持